- Iterate
- Job Titles
- Who Reports to the CEO?
Table of contents
At most companies, every member of the C-suite reports to the Chief Executive Officer (CEO). But the number of direct reports depends on the company’s organizational structure.

What is the CEO?
The CEO is the most senior officer at a company. They’re the face of the company both externally for the public and internally for the organization’s employees. Effective CEOs have strong leadership and delegation skills to set and execute the vision for their company. These same skills are important in getting buy-in from their employees.
As one consumer goods CEO told McKinsey, “You are speaking through an extraordinary amplification system. The slightest thing you do or say is picked up on by everyone in the system and, by and large, acted on.”
CEOs are the leaders in charge of guiding the ship. They establish an organization’s overall priorities, strategies, and frameworks. With that strategy in mind, it’s up to the C-suite team to implement the CEO’s vision throughout the organization.
Some CEOs also hold the title of President, like Shantanu Narayen, President and CEO of Adobe.
CEOs also serve as the main liaison between the board of directors and corporate operations and are often members of their company’s board.
Who reports to the CEO?
At most companies, the CEO’s direct reports are the other C-suite members. However, non-C-suite management may also report to the CEO.
What is the C-suite?
The C-suite is made up of a company’s top-ranking executive employees. The “C” stands for “Chief,” and refers to the fact that every member of the C-suite sits at the top of their respective department and answers directly to the CEO.
While all members of the C-Suite report to the CEO, not every direct report to the CEO has to be in the C-Suite. Vice presidents (VPs) and senior vice presidents (SVPs) who generally report to lower-level C-suite members might sometimes report directly to the CEO.
In addition to the CEO, most C-suites in a company include:
- Chief Operating Officer (COO): The COO is usually the CEO’s second-in-command. They’re charged with overseeing the day-to-day operations of the organization and implementing the plans laid out by the CEO. When there is no COO position, the CEO tends to be more hands-on, and VPs and SVPs are more likely to report directly to the CEO.
- Chief Financial Officer (CFO): The CFO is responsible for managing a company’s finances. They look out for their CEO’s priorities by creating efficiencies and delivering cost savings whenever possible to help further the organization’s financial gain.
- Chief Marketing Officer (CMO): The CMO is responsible for the company’s marketing efforts. The CMO works closely with the CEO to determine how the company should position its brand.
- Chief Technology Officer (CTO): The CTO leads the company’s technology or engineering departments as well as research and development (R&D).
- Chief Information Officer (CIO): The CIO is in charge of building, maintaining, and developing an organization’s IT infrastructure.
- Overall, these roles exist to guide a company’s various departments toward the CEO’s vision. The C-suite and the CEO’s other direct reports work with each other and the CEO to align every department — so the entire company can successfully move toward its goals.
Who does the CEO report to?
The CEO reports to the company’s board of directors. The board of directors is an elected group that represents shareholder interests.
All public companies are required to have a board of directors. Different states have different requirements for when and how corporations should establish their boards.
Who reports directly to the board of directors?
The CEO is the only company employee who reports directly to the board of directors. The board of directors acts as the CEO’s boss — they have the power to hire or fire the CEO. The board must sign off on any important strategic or financial decisions.
Most members of the board are external to the company since they’re meant to act in the shareholders’ best interests, and not those of the C-suite or employees.
CEO vs. chairman
The head of the board of directors is the chairman. The board of directors elects a chairman to preside over board meetings. The chairman works to reach a consensus in board decisions and can have significant sway in board voting.
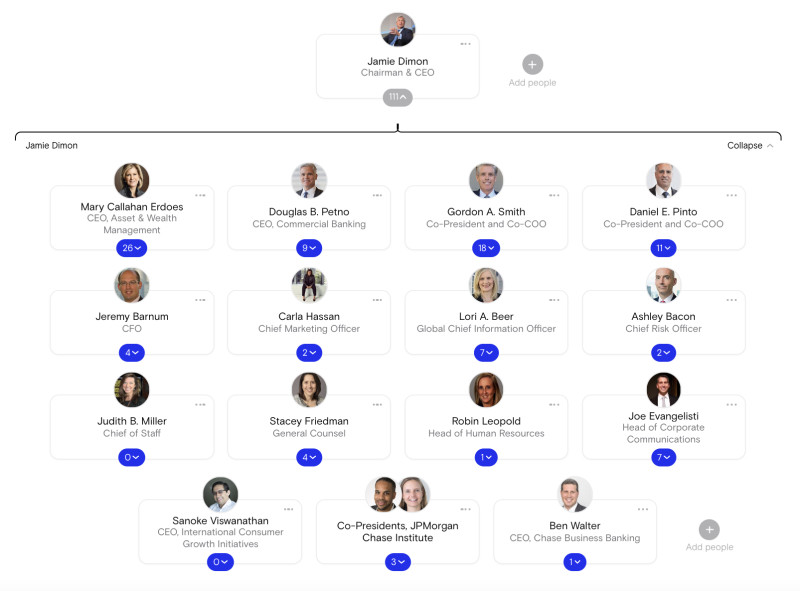
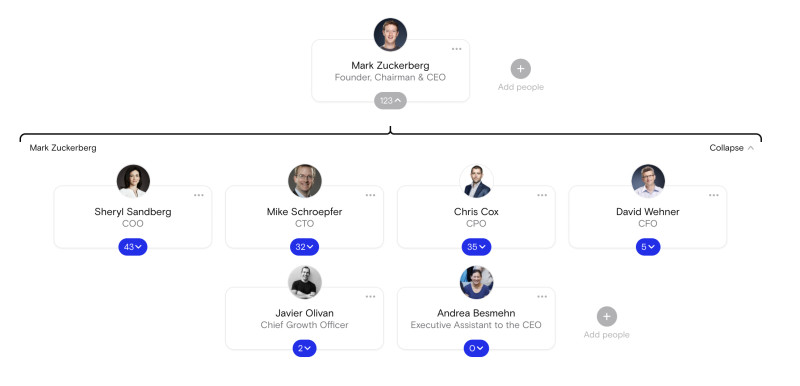
At some companies, the CEO is also the chairman. At Meta, for example, Mark Zuckerberg holds the titles of Founder, Chairman, and CEO. Similarly, Jamie Dimon is both the Chairman and CEO of JPMorgan Chase.
The JPMorgan Chase organizational chart. Jamie Dimon, Chairman & CEO, has 16 direct reports.
Meta’s organizational chart. Founder, Chairman, and CEO Mark Zuckerberg has 6 direct reports.
This structure can mean fewer checks and balances for the CEO. The chairman and the board are meant to oversee the CEO and C-suite, but when the CEO and C-suite are one and the same, there’s less accountability and transparency. When the chairman is separate from the CEO, the chairman tends to stay behind the scenes, while the CEO is the public face of the company.
CEOs in organizational charts
To give you a better idea of the CEO reporting structure and who reports to the CEO, here are three more organization chart examples:
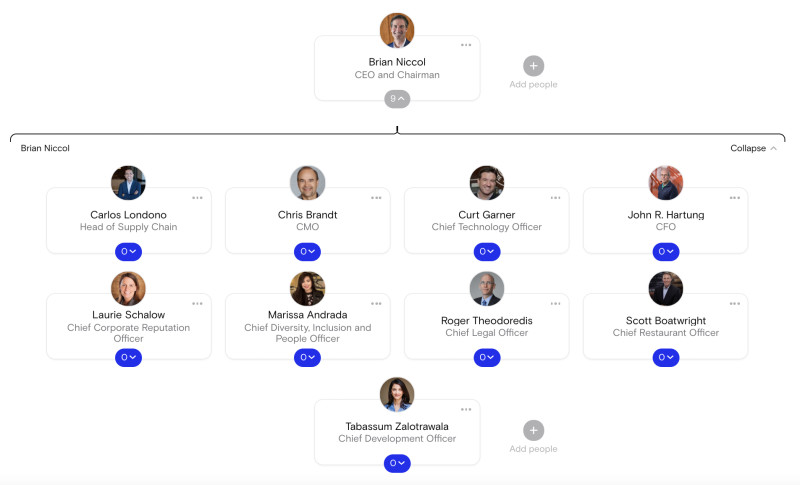
1. Chipotle
Chipotle’s org chart is a classic example of who reports to the CEO: 8 of CEO and Chairman Brian Niccol’s 9 direct reports are members of the C-suite.
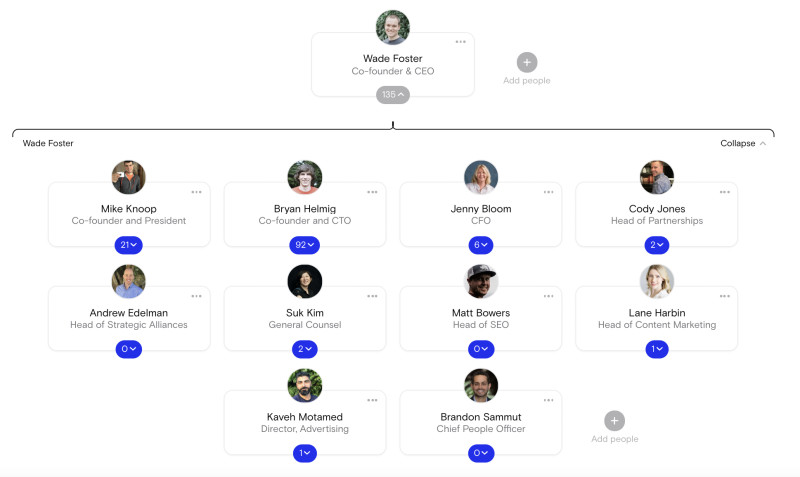
2. Zapier
Zapier is a global remote company that allows end-users to integrate web applications.
Zapier’s org chart is a great example of both C-suite and non-C-suite direct reports to the CEO. Co-founder and CEO Wade Foster has 10 direct reports, ranging from fellow C-suite members to senior leadership with more specific focuses, such as “Head of SEO.”
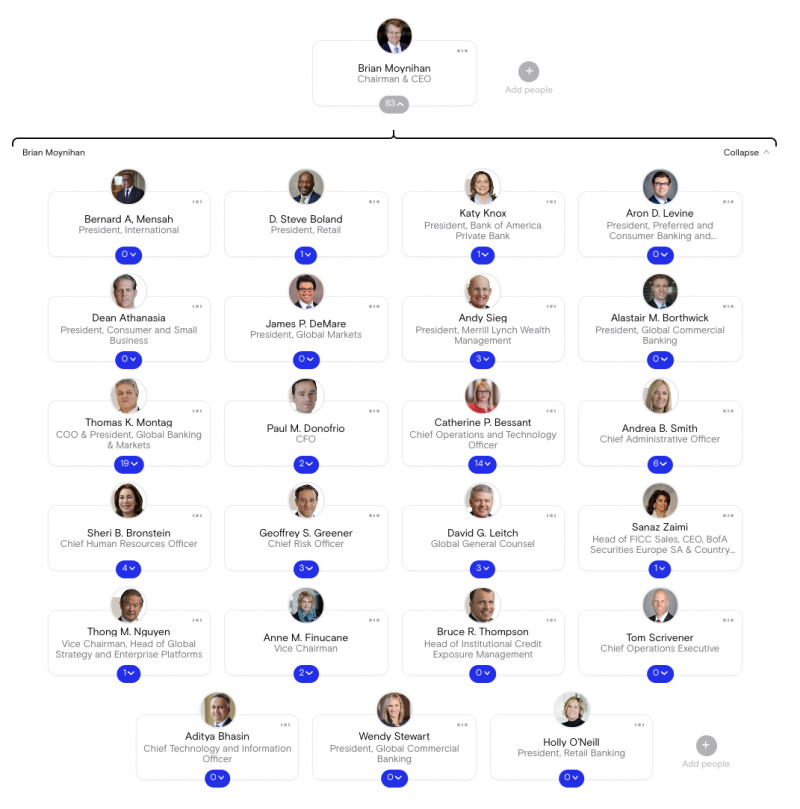
3. Bank of America
Bank of America (BoA) is a multinational investment bank and financial services company with several subsidiaries, so their org chart is a little bit different from a smaller company. Direct reports of Chairman & CEO Brian Moynihan include Vice Chairmen of the BoA board of directors, fellow C-suite members, and the presidents of BoA’s various subsidiaries.
Want to explore more org charts across our website? Make a (free) account and join your company to see more!