- Iterate
- Job Titles
- Product Manager
Table of contents
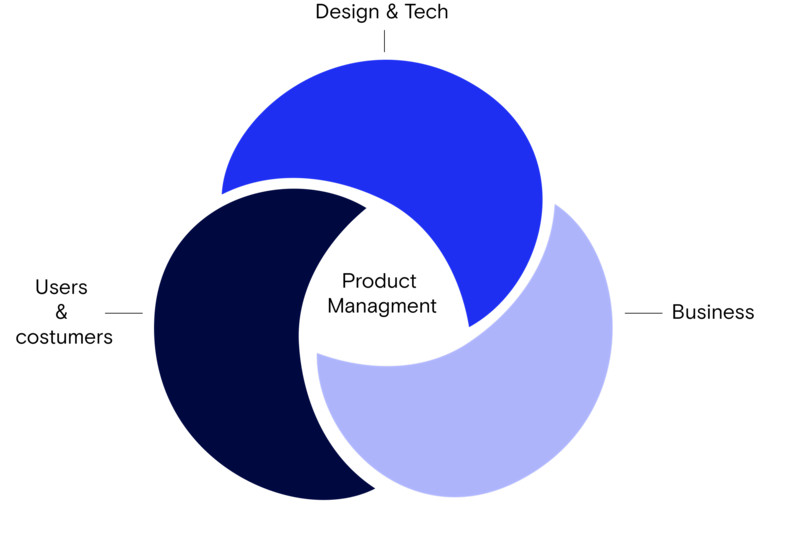
What is a product manager? They’re often described as something like a Venn diagram where design, tech, customers, and the business intersect.

Product management is an exciting career with loads of opportunities. According to a December 2021 article, Product Manager ranks tenth for "roles with the greatest number of LinkedIn job posts in Q3 2021."
This article explores product management, what the role entails, the skills you need, what product managers earn, and how to become a product manager.
What Does a Product Manager do?
Product managers are responsible for the launch and continuous evolution of a digital product. They must outline a vision (or product roadmap) and develop a strategy to achieve the product's goals and objectives.
Product managers must analyze the market, customers, and competitors to formulate a product's strategy. They also work closely with UX designers and researchers to identify user pain points and prioritize design solutions for release.
Product management is a cross-functional leadership role. Managers must work with team members from various departments, including UX, engineering, sales, marketing, and customer support.
People often describe product managers in a Venn diagram where design/tech, customers, and business intersect to form product management.
Product Managers in the Wild
It’s one thing to know the requirements of a role — it’s another to see what that role looks like in the wild. At The Org, we believe that putting a face to the job title and seeing for yourself where the role fits into the company makes it much easier to picture yourself in it.
Where in the company hierarchy does product managers fit in? Who are their closest team members, and who do they report to? What career growth opportunities does product managers have within the company structure?
We’re here to help you answer those questions. Explore live positions for product managers and see the role in the wild here.
Product Manager vs. Project Manager
While there are a lot of parallels and similarities between product management and project management, they are completely different roles.
In the context of product management, the product manager is in charge of the entire product, while a project manager will oversee specific projects–like the end-to-end process of developing a new feature.
Product Manager's Responsibilities
As a cross-functional team leader, product management is a multi-faceted discipline. Here are some of a product manager's primary responsibilities.
Conducting Research & Identifying Opportunities
Before a product manager can strategize effectively, they must understand the landscape. Customer and competitor research helps product managers understand the market to develop a competitive product strategy that serves users.
Customer reviews and feedback sessions are essential for product managers to understand how people use the product, their pain points, expectations, and other customer-centric viewpoints.
Product managers also conduct internal research, like the product's analytics and customer support tickets, to identify opportunities for innovation and improvement.
Outline the Product Roadmap
The product roadmap outlines the product's vision, strategy, and priorities over time. This working document identifies the short-term goals and objectives towards meeting the product's long-term goals.
Product managers must combine research data with feedback from various departments to identify and prioritize the product's releases. At the same time, they must also consider the product life cycle to prolong its success and avoid its inevitable decline for as long as possible.
To complicate matters, product managers must also include product fixes like usability and accessibility issues into the release plan. These time-consuming yet crucial releases can impact or delay product goals.
Executing Strategy
Product managers must work with design, engineering, sales, and marketing to execute each stage of the product roadmap. They delegate tasks and responsibilities and manage workflows.
The product roadmap rollout requires an acute understanding of project management so that product managers can coordinate and align departments to meet deadlines.
They must ensure a smooth handoff from product designers to engineers while working with sales and marketing to deliver a return on investment.
Budget & Revenue Management
As if all of the above wasn't challenging enough, product managers must oversee the product's budget and work within its constraints. They're also responsible for growing the product's revenue, increasing profits, and managing costs.
Product managers must ensure that the product and feature releases deliver a positive return on investment.
What Makes a Good Product Manager?
There are three essential product management skills:
- Communication
- Business
- Research
Let's take a look at each of these and other skills a product manager must have in greater detail.
Excellent Communication
Outstanding leadership requires excellent communication. Product managers must communicate with team members (from all backgrounds and disciplines), customers, and stakeholders. Their communication skills must include verbal, video calls, emails, phone, face-to-face interactions, and even public speaking.
This communication doesn't only involve talking but actively listening to fully understand and comprehend customer and team member issues.
Business Acumen
Product managers manage a product like it's a business within the organization. The product has its own budget, team, strategy, goals, customers, and other business components that are often separate from the rest of the company.
Product managers must possess the business expertise to scale and optimize a product in highly competitive marketplaces to deliver a positive return for the organization.
Research
Research and testing are crucial for a product manager to make the right decisions. They must be obsessed with researching their market, competitors, and customers to find opportunities.
Curious and Eager to Learn
Product managers are generalists rather than specialists and therefore must be eager to learn as much as possible about their product, customers, team members, technologies, workflows, market trends, and competitors.
Leadership
Leadership is a vital product management skill. Managers often lead cross-functional teams of specialists and must always make confident decisions and deliver clear instructions.
Product managers must also motivate teams during challenging projects or meet tight deadlines.
User Experience
Understanding user experience and design thinking can help product managers empathize with customers to solve their problems more effectively. While UX designers are primarily responsible for the user experience, product managers can use this knowledge to prioritize the product roadmap and align business value opportunities.
How Much Does a Product Manager Earn?
According to Glassdoor, the average base salary for a Product Manager in the United States is $113,446. At the low-end, product managers can expect to earn $73k while the highest earners get paid around $175k.
What are the job requirements of a product manager?
The job requirements for a product manager typically include:
- Strong communication skills to communicate their product vision and strategy to team members, customers, and other stakeholders.
- Being able to analyze data and metrics to evaluate product performance and make data-driven decisions.
- A deep understanding of customer needs and preferences and the ability to develop products that solve their problems and create value.
- An understanding of the industry and market trends, and the ability to identify emerging opportunities and threats.
- Proficiency in strategic thinking with the purpose of developing and executing a product strategy that aligns with business goals and market trends and identifies growth opportunities.
- A basic technical understanding of the product development process and the ability to work closely with technical teams.
How to Become a Product Manager?
At The Org, we believe in increasing transparency in recruitment and hiring. That’s why we strive to make it easier for top talent to find where they fit in. Explore more than 400,000 organizations, and stay up to date with open positions with The Org.
Product managers generally hold a bachelor's degree in business, design, or tech fields. While there is no specific bachelor's degree requirement, some product management roles may insist on technical background or experience.
Due to the complexities of the job, many product managers recommend taking a product management course to understand the role and employer expectations better. HubSpot has an excellent article with a list of 16 product management courses, including online and physical attendance options.
You can also apply through Associate Product Manager (APM) programs designed by the world's biggest tech companies to train new grads. These programs typically run for a few years, giving you a fantastic foundation for your product management career. You can find a comprehensive list of companies at APM List, including Apple, Google, Facebook, Salesforce, Disney, and many more.
If you're looking to get promoted within your organization, we highly recommend learning programming fundamentals like HTML, CSS, and Javascript.
There are tons of courses and resources, including free YouTube videos, that teach programming basics. You don't have to learn how to develop a website or application, but programming knowledge will help you understand your product's technical constraints and communicate with engineers better.
Hiring a product manager
Is your org looking to hire a product manager?
If so, you may benefit from reading our comprehensive 10-step guide on recruitment and hiring. In this guide, you’ll learn all about the hiring process. From writing your job description, to developing candidate sourcing strategies, to common interview questions, to writing a job offer letter — we’ve got you covered from start to finish.
At The Org, we believe traditional recruiting is in need of a refresh. Candidates want to know who they’ll work with, not just what they’ll do. Workplace culture, interpersonal relationships, and company values are more important now than ever.
And what better way to showcase your company’s unique culture than through your Org Chart?
Highlight different teams in your organization, the people that make these teams great, and show candidates how they fit into the big picture.
Your Org Chart is a novel and effective way to show candidates where they fit in, and to show off your greatest asset: your people.
Explore Org Charts here, and sign up today to create your own customized Org Chart for your company.


The ORG helps
you hire great
candidates
Free to use – try today